Mobile Telephony and Safety
FIND OUT MORE
At COSMOTE our greatest commitment
is ensuring safety for all.
On a daily basis, millions of minutes of speech, messages and data are transmitted through ,
the mobile network, while the needs for communication and entertainment are constantly increasing.
Source: Focus Bari, Panhellenic research in M-F, 13-74yrs, January - March 2021
As the operator of the largest mobile network in Greece, our priority is
to meet the ever-increasing needs of our customers by offering them high-speed mobile Internet and adequate coverage, wherever they may be,
but also to ensure the safety of everyone using our infrastructure.
How does mobile
telephony work?
A mobile telephony network consists of a number of Base Stations, commonly referred to as “antennas”.
Each antenna covers a particular geographical area which resembles a cell when depicted on a map. The antenna can only serve a specific volume of traffic (calls, data, etc.) at any one time.
Base stations are connected to each other but also to the telecommunication centers, managing both voice calls and data, which are then forwarded to antennas or other networks (e.g., fixed telephony) via a two-way communication system.
Users can move around during a call without interruption in their communication, since the network has been designed to transmit the signal from antenna to antenna.
Mobile
Telephony Networks
Currently, the mobile communication systems used in Greece are 2G, 3G and 4G technologies. Recently, COSMOTE launched, first in Greece,5G network.
3G
Offering increased data capacity, 3G systems made multi media services, video calling and Mobile Internet, available to mobile phone users.
4G
Then 4G offered, much higher speeds and enabled users to tap into a wide variety of improved mobile phone applications - such as high definition (HD) video, teleconferencing and new gaming services.
5G
5th generation (5G) systems are an extremely important development in the history of mobile communication networks. Through them, data will be transferred 10 times faster than today thus enabling almost real-time communications, while network capacity will also be increased considerably.
5G is designed to meet the enormous data growth and connectivity needs of today's society and to effectively support billions of Internet of Things devices connected simultaneously as well as innovative applications that will dramatically change the way we live and work.

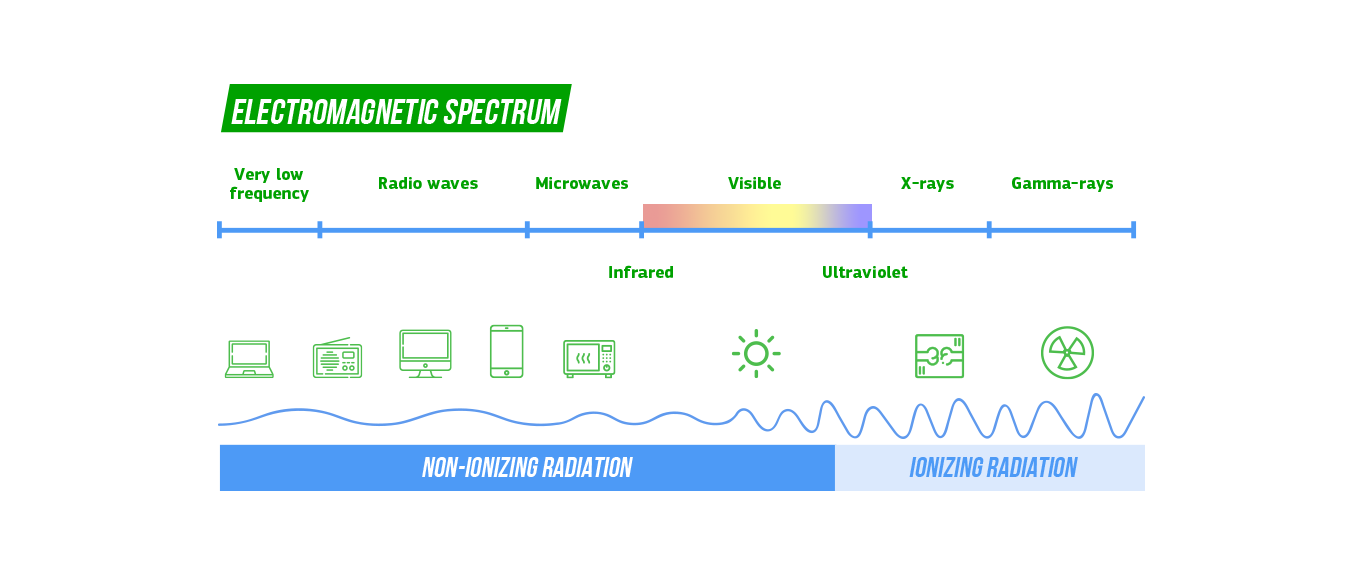
Radiation & Mobile Telephony
Mobile phones and base stations emit a type of electromagnetic radiation known as radio frequency waves, that is, a form non-ionizing radiation that has nothing to do with radioactivity.
Sunlight, the earth’s magnetic field, the fields created by electrical devices as well as the electromagnetic waves involved in the transmission of radio and television signals belong to the same type of EMF radiation.
At OTE Group, we consistently and responsibly comply
with national and international safety
guidelines at every stage of design,
construction and operation of our mobile telephony networks.
In order to protect the public from exposure to electromagnetic fields, the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP), has thoroughly reviewed a large volume of research and epidemiological studies examining the effects of 24-hour continuous exposure to electromagnetic waves. The studies were targeted at the general population and included also vulnerable groups (children, people with health conditions, the elderly).
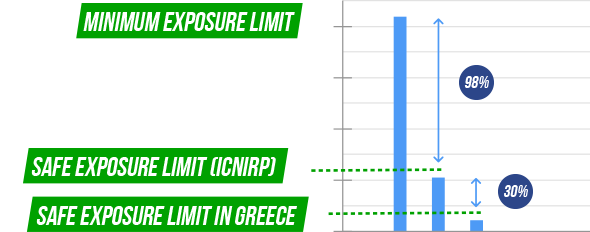
As a result of this review, the ICNIRP was able to determine the minimum exposure limit, which was then reduced by 98%, in order to establish the Commission’s safe exposure limits recommendations.
The international and national exposure guidelines and regulations currently in place refer to electromagnetic fields utilized by all 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G technologies as well as other radio frequencies such as radio and television broadcasts.
Greece is one of the countries which have decided to apply limits that are even stricter (by 30%) than the European recommendation, thus creating a supplementary safety coefficient.
The World Health Organization (WHO), the EU Scientific Committee on Emerging and Newly identified Risks (SCENIHR) and the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) have all come to the following conclusion:
"Exposure to EMF radiation related to wireless networks and their use does not produce any adverse effects on the health of the population provided it remains below the levels recommended by the ICNIRP"
[WHO 1993, SCENIHR 2015, ICNIRP Guide lines 2009, WHO 2013, ICNIRP Guidelines 2018, ICNIRP Guidelines 2020]
"Providing that the overall exposure from 5G remains below international guidelines, no consequences for public health are anticipated".
The GSMA (Global Association of Mobile Telephony Providers) has created a video (June 2020) regarding the electromagnetic fields and the safety factors related to the use of mobile networks, which provides information based on the latest international safety guidelines.
Greek Atomic Energy
Commission (EEΑE)
It is the national regulatory authority responsible for controlling, regulating and supervising all activities related to nuclear energy, nuclear technology and radiology, and for ensuring nuclear safety and protection from radio protection. You can see the Commission’s report on EMF radiation
here.
Hellenic Telecommunications & Post Commission (EETT)
EETT is an Independent Administrative Authority. It acts as the National Regulator that monitors, regulates and supervises: (a) the electronic communications market, within which fixed and mobile telephony, wireless communications and Internet access providers operate and (b) the postal services market, within which postal and courier service providers operate. The EETT’s report on radiation is available
here.
WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION (WHO)
The WHO is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. Engaging a broad range of scientists (epidemiologists, biologists, physicists, engineers), its purpose is to coordinate and promote international medical research as well as to provide information and advice related to public health. The WHO’s report on electromagnetic fields is available
here.
FAQs
What kind of radiation is emitted from mobile phone antennas and cell phones?
Radiation is the emission of energy in the form of waves or particles. Depending on the type of energy and the effect it has on matter, it is divided into two major categories: ionizing and non-ionizing. The radiation emitted from cellular antennas and mobile phones is of the radio frequency type, and it is non-ionizing. The electromagnetic waves used to transmit radio and television signals as well as the ones utilized in radar systems belong to the same category.
Is this radiation radioactive?
No. Electromagnetic radiation has nothing to do with radioactivity. Electromagnetic radiation from mobile phones and cellular antennas is part of non-ionizing radiation, which does not damage biological cells.
The kind of radiation that could potentially be harmful for human health is ionizing radiation, for example Gamma-rays, X-rays and ultraviolet light.
Are there limits in place for the exposure to this radiation? How these limits have been set?
The ICNIRP (International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection) is an independent, internationally reputed scientific committee whose work centers on protecting the public from non-ionizing radiation. As a non-governmental committee officially recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the European Union, it brings together experts from different countries and disciplines - such as Biology, Epidemiology, Medicine, Physics and Chemistry- who assess the risk of exposure to electromagnetic fields and provide guidance with setting the limits that will guarantee the safety of the general public.
The ICNIRP, after reviewing all published research on the biological effects of electromagnetic radiation, concluded that the only effects that could be used as a basis for establishing human exposure limits were those due to the short-term rise in tissue temperature from the absorption of electromagnetic energy by the human body. This review served as the basis for determining the minimum exposure level.
Taking into account that certain population groups may be more vulnerable than others, the ICNIRP proposed the introduction of public exposure limits, opting for a 98% reduction in the minimum exposure level.
What is the legal framework in Greece?
In Greece, State has opted to adopt stricter limits (by 30%) than those proposed by the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP), thus creating a supplementary safety coefficient.
When special conditions apply, for example when a nursery/kindergarten, school, hospital or nursing home are situated at a distance of less than 300m from an installed antenna, the Greek State has optionally set 40% stricter limits than the ones proposed by the ICNIRP (Law 4635/2019, replacing 4070/2012).
Greece is one of the EU countries that have set stricter limits than those set out in the relevant EU Council recommendation.
In any event, the criteria for adopting lower exposure limits are the result of political decisions and have not been adopted on the basis of specific scientific data.
What about other countries in the world?
The ICNIRP limits have been adopted in most European countries, as well as in the USA, Australia and New Zealand.
Greece, Switzerland, Italy and certain Eastern European countries such as Bulgaria have chosen to adopt stricter limits. Moreover, recently countries with stricter limits like Romania and Poland adopted ICNIRP limits.
The WHO has launched an effort to harmonize exposure limits around the world.
In either case, the criteria for setting lower exposure limits in the countries where these have been applied, including Greece, are the result of political decisions and were not adopted on the basis of specific scientific data.
Which is the competent body that is responsible for scientific measurements in Greece?
The Greek Atomic Energy Commission (EEAE) is responsible for the protection of the general population from non-ionizing radiation.
Based on aggregate data gathered following ad-hoc measurements by EEAE in urban areas where mobile telephony base stations have been installed, full compliance of the safety exposure limits were recorded. The exposure levels from all sources (radio, television, mobile telephony, wireless internet networks etc.) were found to be from tens to thousands of times below the set safety limits.
According to the new legislation, the EEAE is expected to ensure compliance with the limits of safe exposure to electromagnetic radiation, conducting inspections ex officio or at the request of the Hellenic Telecommunications and Post Commission (EETT) or of any natural or legal person with a legitimate interest.
What is the National Observatory of Electromagnetic Fields (EPIP)?
The EAEE has developed a program of continuous radiation measurements, the National Observatory of Electromagnetic Fields (NOEF). The NOEF’s role is to continuously monitor compliance with the established limits of safe exposure to electromagnetic fields via an interconnected system of fixed and mobile measurement stations measuring the values of electromagnetic radiation.
Does COSMOTE perform radiation measurements?
COSMOTE cooperates with all ISO 17025: 2017-certified bodies for the performance of ad hoc EMF measurements.
In addition, with a view to performing reliable and objective measurements, COSMOTE is the owner of a measurement laboratory certified to ISO 17025: 2017 by the National Accreditation System (ESYD).
At the same time, we work together with university institutions in order to carry out continuous, 24-hour measurements. The universities are responsible for the installation of special monitoring systems in the vicinity of base stations, which record electromagnetic field values on a 24-hour basis. The results are accessible to the public on www.pedion24.gr
How does mobile telephony work?
Mobile phones work by sending and receiving low power radio signals. These signals are sent and received by antennas, also known as mobile base stations. Base stations connect to other mobile and landline networks and transmit the signal/call to these networks.
Why do we need a dense network and more antennas?
The emmission power of a mobile phone increases and decreases depending on how easy or difficult it is to communicate with the base station.
The denser the network of base stations, the easier it is for the mobile phone to communicate with the network, thus reducing the emmission power transmitted by it. For that reason, it is in effect better to have a dense network of stations.
How does an antenna transmit the signal?
The antennas transmit straight, with a slight downward tilt.
The field strength just below the antennas is much lower than that measured directly in front of the antennas.
What are the consequences of removing antennas from a certain area?
Antenna removals make it more difficult for mobile phones to connect to the network. As a result, the device automatically increases its emmission power in order to establish communication.
At the same time, the network’s capacity to serve customers in this area is significantly reduced.
What are the different types of mobile technologies?
In addition to traditional voice calling, wireless technology has made significant advancements in recent years, facilitating the emergence of many applications that brought on important changes to our everyday lives. The mobile technologies currently available are 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G, which COSMOTE launched first in Greece.
3G allowed the use of multimedia, video calling and brought mobile internet into our lives.
The next step was the arrival of 4G technology, enabling the use of mobile broadband and high-speed data through which users were able to tap into a variety of enhanced applications, including HD video and online gaming services.
5G, the 5th generation of mobile networks, is not simply an enhanced version of existing technologies. It is one of the fastest and most reliable technologies we have known to date, offering very high data speeds, significantly increased capacity and almost zero response time (latency). 5G is designed to meet the enormous data growth and connectivity needs of today's society and to effectively support billions of parallel Internet of Things devices as well as innovative applications that will dramatically change the way we live and work.
Will 5G work as an autonomous network?
5G will initially coexist with current networks, before gradually evolving into a fully autonomous network. As a result, part of this technology will operate at spectrum frequencies already existing and utilized, and only part of it will make use of higher frequencies (> 24GHz).
Is 5G more dangerous for human health compared to other mobile telephony systems?
One of the main characteristics of electromagnetic fields is that the higher the frequency, the smaller the depth of penetration into the human body. As 5G technologies use higher frequencies, they produce relatively superficial exposure, with smaller percentage penetrating the human body as compared to previous mobile technologies.
Another key feature of the 5G wireless standard is that it uses beam technology, which allows the electromagnetic waves to focus on a specific spot (e.g., on a person using a mobile phone) rather than spreading over a larger area.
In this way, the same frequencies can be sent to different users at the same time without interfering with each other, therefore increasing the rates of communication - as the frequency band does not need to be "shared" among users - but also significantly reducing human exposure to EMF in areas where no communication is required.
Have competent bodies published reports on the effects of 5G technology?
Both the ICNIRP, the independent scientific committee whose work centers on protecting people from exposure to non-ionizing radiation, and the World Health Organization (WHO), are closely monitoring research into electromagnetic fields and their potential effects on human health, immediately reporting on any new findings.
It is important to note that, in early 2020, the ICNIRP stated that none of the frequencies used by mobile communications, including 5G, required no changes to the safety guidelines issued in 1998.
Are there any links between 5G technology and the COVID-19 pandemic?
In an announcement issued in April 2020, the ICNIRP and the World Health Organization stated:
"Some have argued that exposure to electromagnetic fields generated by 5G devices may cause a person to become ill with COVID-19 and increase the severity of the disease. These claims are not supported by any evidence (not even weak evidence) and the vast scientific knowledge on the subject of electromagnetic fields related to 5G networks proves that these claims are unsubstantiated. Exposure to 5G devices does not cause COVID-19, nor does it affect the disease’s development or the health effects of those infected with the new coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), which causes COVID-19. According to World Health Organization experts, for a person to become infected with SARS-CoV-2, he or she must naturally come in contact with the coronavirus and since electromagnetic fields produced by 5G networks cannot carry viruses, it follows that they cannot bring someone into contact with the virus".
What kind of applications will be introduced with the switch to 5G?
5G is expected to introduce a wide range of innovative applications that will change the way we live, work and entertain ourselves. The features of the new 5G mobile technology will enable the first-time use of remote surgery, live holographic telephone calls, entertainment and training via AR (Augmented Reality) & VR (Virtual Reality) without cables and delays, remote drone operation in emergency situations but also the development of smart cities in which driverless cars will become a reality. Most importantly, however, it will pave the way for the emergence of applications and solutions that we are yet to imagine.
When do mobile phones transmit power?
Mobile phones transmit power during telephone communications.
When on Stand By mode, they transmit a short pulse to the network every few minutes to indicate that they are in the specified coverage area and that they are available for receiving calls/data.
What is the amount of radiation emitted by mobile phones?
The total amount of electromagnetic radiation emitted by a mobile phone is relatively small.
In addition, mobile phones have an automatic control system that limits the transmitted power to the minimum amount required for the device to establish a communication with the base station. This achieves energy savings resulting in improved battery life and increased use and standby time for the device, while minimizing interference with other radio communications.
The SAR (Specific Absorption Rate) value is used to measure the energy a person absorbs when using the mobile phone.
The ICNIRP has set a SAR limit of 2W. This is also the limit that has been adopted by the EU and Greece.
Where can I find the SAR value for my mobile phone?
Mobile phone manufacturers cite the SAR measurements applying to each specific device in their specifications and user manuals.
For COSMOTE devices, the SAR value list is available in COSMOTE and GERMANOS physical stores and can also be viewed here.
How can I reduce my mobile phone exposure?
- Reduce the length of your conversations when placing calls from your mobile.
- Use hand release accessories (handsfree or bluetooth) and avoid keeping your mobile phone too close to your body.
- Avoid making and receiving calls when you are in an area with low reception. Instead, place calls from places where the signal is stronger, to ensure your mobile phone uses the minimum amount of power required to establish communication with the base station.